EMBRACE Highlights
NON-INVASIVE:
Obtain a result by only analysing the culture medium in which the embryos are growing
PRIORITISATION SYSTEM:
Provides helpful information about which is the best embryo to transfer, without discarding any embryos

UNIVERSAL:
Good results in fresh & frozen cycles, IVF and ICSI, by following the specific embryo culture protocol
What is the EMBRACE test?
- EMBRACE is a prioritisation system based on the analysis of embryonic cell-free DNA released by blastocysts into the surrounding medium during culture in the IVF laboratory.
- The analysis of one drop of culture medium in which the embryo has been developing, otherwise discarded in standard practice, helps clinicians determine which is the most suitable embryo to transfer.
What information does EMBRACE provide?
- EMBRACE is used for chromosomal aneuploidy detection; the aim of the test is to identify the presence of aneuploidy in embryonic cell-free DNA (detection limit: 10Mb).
- For each blastocyst, one culture medium sample is analysed. The algorithm developed by Igenomix uses that result to determine the probability of the blastocyst having a euploid trophectoderm sample.
- This probability, called euploidy score (ES), is used to establish an order of priority for embryo transfer: the embryo with the highest euploidy score will be recommended first for transfer.
- Clinics can choose from several different types of reports, depending on clinician preferences, legislative guidelines, and regional ethical standards.
How does EMBRACE work?
EMBRACE pathway for fresh or previously vitrified blastocysts
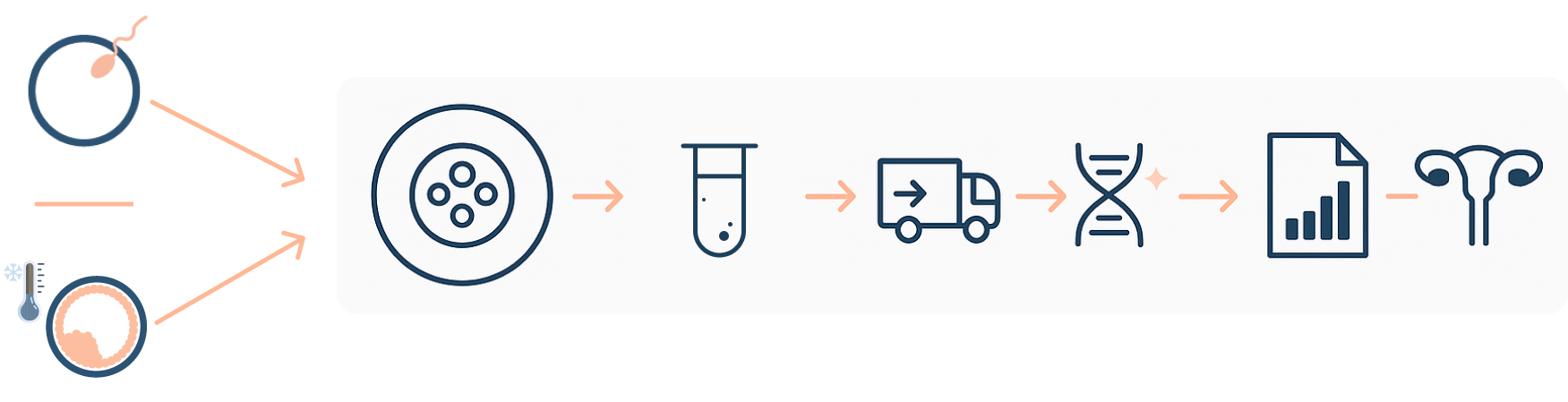
Embryo culture (EMBRACE protocol) → Media collection → Shipping and Sample analysis → Prioritisation report → Transfer according to report
Key aspects:
- EMBRACE is a prioritisation system based on the analysis of the embryonic cfDNA released by the blastocyst to the drop of culture media.
- It helps you decide the best embryo for transfer.
- EMBRACE is not a substitute for PGT-A based on trophectoderm biopsy.
- Culture medium aspiration takes place on day 6 (or 7) of development. Therefore, embryos must be cultured until day 6 (or 7), with a media change taking place on day 4.
- EMBRACE is used for aneuploidy detection only. It is not suitable for structural rearrangements or monogenic disorders testing (PGT-SR/PGT-M).
- EMBRACE can be applied to fresh cycles or previously vitrified day 5/6 embryos.
- EMBRACE can be applied to blastocysts from IVF or ICSI cases cultured in any type of media or incubator (conventional or time-lapse with individual wells).
- To perform EMBRACE, IVF clinics need to pass a validation (dry-run).
Publications List
Non-Invasive Preimplantation Genetic Testing.
Bakalova DN, Navarro-Sánchez L et al. Genes. 2025; 16(5): 552.
The impact of implementing a non-invasive preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidies (niPGT-A) embryo culture protocol on embryo viability and clinical outcomes.
Sakkas D, Navarro-Sánchez L et al. Human Reprod. 2024; 39(9): 1952–1959.
Culture time to optimize embryo cell-free DNA analysis for frozen-thawed blastocysts undergoing noninvasive preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy.
Ardestani G, Banti M et al. Fertil Steril. 2024; 122(3):465-473.
Human embryo live imaging reveals nuclear DNA shedding during blastocyst expansion and biopsy.
Domingo-Muelas A, Skory RM et al.Cell. 2023; 186(15):3166-3181.
Link to publicationNon-invasive preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidies: an update.
Navarro-Sánchez L, García-Pascual C et al. Reprod Biomed Online. 2022; 44(5):817-828.
Multicenter prospective study of concordance between embryo cell-free DNA and trophectoderm biopsies from 1,301 human blastocysts.
Rubio C, Navarro-Sánchez L et al (2020). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020; 223(5):751.e1-13.
Embryonic cell-free DNA versus trophectoderm biopsy for aneuploidy testing: concordance rate and clinical implications.
Rubio C, Rienzi L et al. Fertil Steril. 2019; 112(3):510-519.
Link to publicationOrigin and composition of cell-free DNA in spent medium from human embryo culture during preimplantation development.
Vera-Rodriguez M, Diez-Juan A et al. Human Reprod. 2018; 33(4):745–756.
Link to publicationPoster Presentations and Abstracts
ESHRE 2024 | Multicenter concordance study of embryo cell-free DNA and trophectoderm biopsies: impact on clinical outcomes.
DownloadASRM 2023 | Consistency of embryo cell-free DNA results with paired trophectoderm biopsies and whole day-6 blastocysts in different culture conditions.
DownloadESHRE 2023 | Impact of blastocyst quality and post-thaw embryo culture factors in non-invasive PGT-A informativity on vitrified blastocysts.
DownloadSEF 2022 | Aplicación clínica del análisis cromosómico preimplantatorio no invasivo basado en el ADN libre embrionario en medio de cultivo en España.
DownloadESHRE 2022 | High concordance of the embryonic cell-free DNA with the inner cell mass: impact of blastocyst quality, patient age and mode of fertilization.
DownloadASEBIR 2021 | Alta reproducibilidad de los resultados del análisis no invasivo de aneuploidías con diferentes tipos de incubador y de medio de cultivo.
DownloadASRM 2021 1st Place Prize Poster | Embryo cell-free DNA highly represents the chromosomal constitution of both the inner cell mass and the trophectoderm of human blastocysts.
DownloadWebinars and Lectures
Listen to Our Users!
IVF culture media refresh in a reduced volume on day 4 aimed at improving non-invasive embryo selection does nor affect embryo competence: a prospective analysis of 2,605 embryos.
Maggiulli R, Cimadomo D et al. Reprod Biomed Online. 2022.
Find out moreESHRE 2024 | P-109: Non-invasive Genetic Testing (niPGTA) and Laser Assisted Hatching (LAH) may improve pregnancy and ongoing pregnancy rates in patients of advanced maternal age
Find out moreESHRE 2022 | P-177: Non-invasive aneuploidy testing versus conventional morphological embryo selection in good prognosis patients.
Find out moreESHRE 2021 | P- 560: Comparative analysis of non-invasive preimplantation genetic testing of aneuploidies (niPGT-A), PGT-A and IVF cycles without aneuploidy testing: preliminary results.
Find out moreFAQs
EMBRACE is a non-invasive test used in combination with in vitro fertilisation (IVF) treatment to prioritise embryos for transfer. The EMBRACE test involves the analysis of embryonic cell-free DNA (cfDNA) released by an embryo into the surrounding media in which it has been cultured. The spent blastocyst media (SBM) is collected on day 6 (or 7) of development and the cfDNA is analysed to assess the copy number for all 24 chromosomes. This information is used to establish an order of priority for embryo transfer, based on the Euploidy Score that each culture media receives. This score has been developed according to the data of thousands of SBM and trophectoderm (TE) biopsy samples analysed at Igenomix and represents the probability of the blastocyst having a euploid trophectoderm result.
The medium in which a blastocyst has been cultured in between day 4 and day 6 (or 7) is placed in a PCR tube (provided by Igenomix) and shipped to the Igenomix laboratory for analysis.
The concordance rate between the cell-free DNA present in SBM and the corresponding trophectoderm biopsy is 93% for a female result and 98% for a male result (Rubio et al, 2020).
Prior to sending research or clinical samples, each IVF laboratory will need to perform a validation of the modified IVF laboratory protocol required for the EMBRACE test. The aim of this validation is to check whether the practitioner is able to consistently perform the EMBRACE procedure and achieve the expected informativity and concordance results. This process is necessary to check if the modified EMBRACE culture conditions have been successfully implemented in the IVF laboratory, without the introduction of external or maternal cell contamination. The modified EMBRACE culture conditions don´t affect embryo viability or potential but imply slight modifications of the standard routine regarding culture volume, washes and moment of vitrification.
The standard EMBRACE validation includes the analysis of spent blastocyst media (SBM) samples and the corresponding trophectoderm (TE) biopsy from clinical PGT-A/-SR cases. Alternatively, discarded whole blastocysts (WB) that are poor quality or abnormally fertilised could be utilised for the validation. The SBM and TE/WB are analysed and the concordance in results is established. Please, contact the EMBRACE team in case the standard validation is not possible in your clinic. We will develop a validation strategy based on your needs.
It is crucial to properly denudate oocytes and perform the wash steps according to the EMBRACE protocol. If cumulus cells are thoroughly removed in the denudation step and subsequent washes are correctly performed, the risk of maternal contamination can be greatly reduced. The presence of MCC may result in incorrect result for the embryo ploidy status, since the maternal cells may interfere with the result and mask an aneuploid result as euploid.
The IVF laboratory will need to move the embryos to a fresh drop at least once – on the morning of day 4 – in both types of cultures. For sequential culture, the change of medium can be done at the same time on the morning of day 4.
We cannot accept SBM from blastocysts that have been cultured only until Day 5 of development. The performance of Day 5 samples is poor, showing lower informativity and concordance rates compared to samples from Day 6 embryos. Blastocysts must be kept in culture at least until Day 6 of development. Embryo viability and potential will not be affected (Sakkas et al, 2024).
It is not mandatory to perform ICSI for EMBRACE. IVF insemination can be performed, as long as zygotes are denuded properly after fertilisation. Sperm DNA does not amplify with our current protocol.
All the medium must be sent to the genetics laboratory. All the medium is used in the first analysis. In the event of a non-informative result, the embryo can be transferred according to prioritisation, or the blastocyst can be thawed again and cultured for 8 hours for re-media analysis.
No, these procedures do not improve the results significantly. We do not recommend them when performing EMBRACE. Some clinics perform zona hatching after thawing blastocysts for transfer to improve the pregnancy rate.
A Euploidy Score is established for each sample. This score has been developed according to data from >1,000 samples analysed at Igenomix and represents the probability of the blastocyst having a euploid trophectoderm result. EMBRACE provides an embryo prioritisation report based on this Euploidy Score. Clinics may also wish to include additional data to the clinic reports, such as detailed chromosomal results for each sample.




