Overview
- Around 3%-4% of newborns are affected by a genetic condition.
- Igenomix NBS identifies genetic disorders in newborn babies.
- Newborn screening is a mandatory public health program that offers screening and follow-up medical care to all newborns for a variety of medical conditions.
- Igenomix Newborn Screening Test is a comprehensive genetic test that analyzes 237 genes using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) technologies allowing a direct approach of genetic disorders to reach a rapid, accurate diagnosis.
- In addition, this test identifies a child is a healthy carrier of any of these genetic alterations.
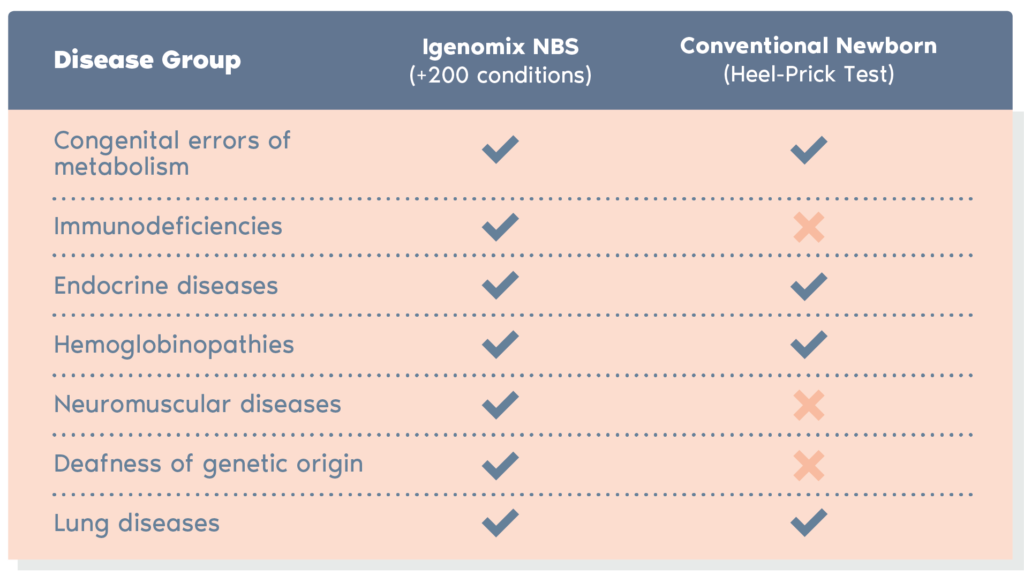
NBS provides an extended panel of disorders analyzed with NGS based technologies offering a wider coverage than NBS done by the NHS.
- These genes are responsible for developmental, genetic and metabolic disorders that cause serious health problems starting in early childhood.
- The ultimate benefit is an early intervention to prevent intellectual and physical disabilities as well as life-threatening illnesses.
- This test allows the detection of many more disorders than with a conventional heel prick test.
Goals of Conventional Newborn Screening (NBS)
The goals of newborn screening are:
- Decrease morbidity and mortality of actionable diseases by performing an early intervention to improve neonatal and long-term health outcomes.
- Provide a universal health service of screening to all newborns.
- Identifying screen-positive newborns
- Diagnosing conditions
- Communication with families
- Referral to treatment centers
- Follow up with long-term outcomes
- Educating physicians and patients.
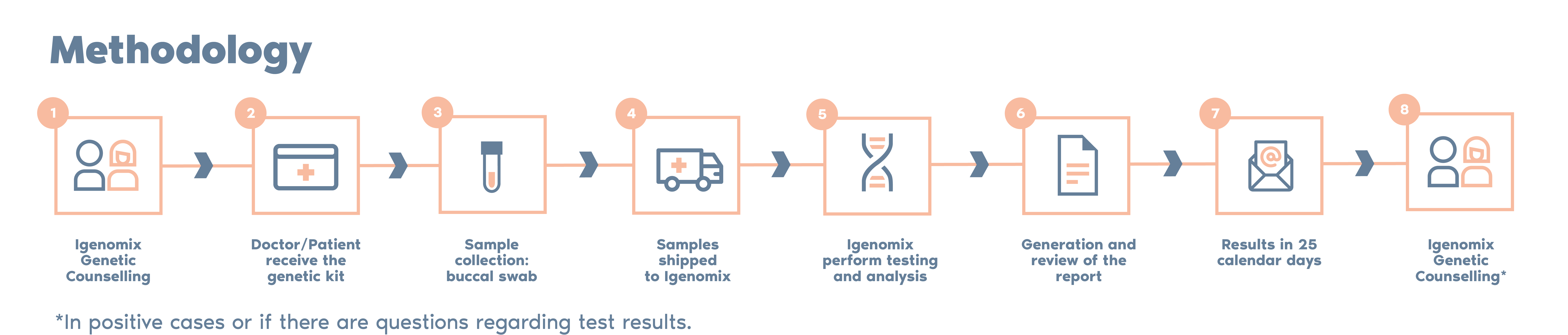
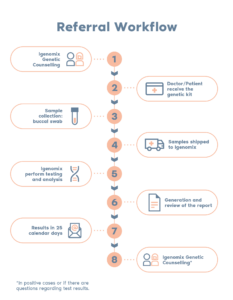
What is the procedure?